Learn everything about herniated discs – symptoms, causes, types, and treatment options. Understand how lifestyle, posture, and aging impact spinal health.
Introduction: What is a Herniated Disc?
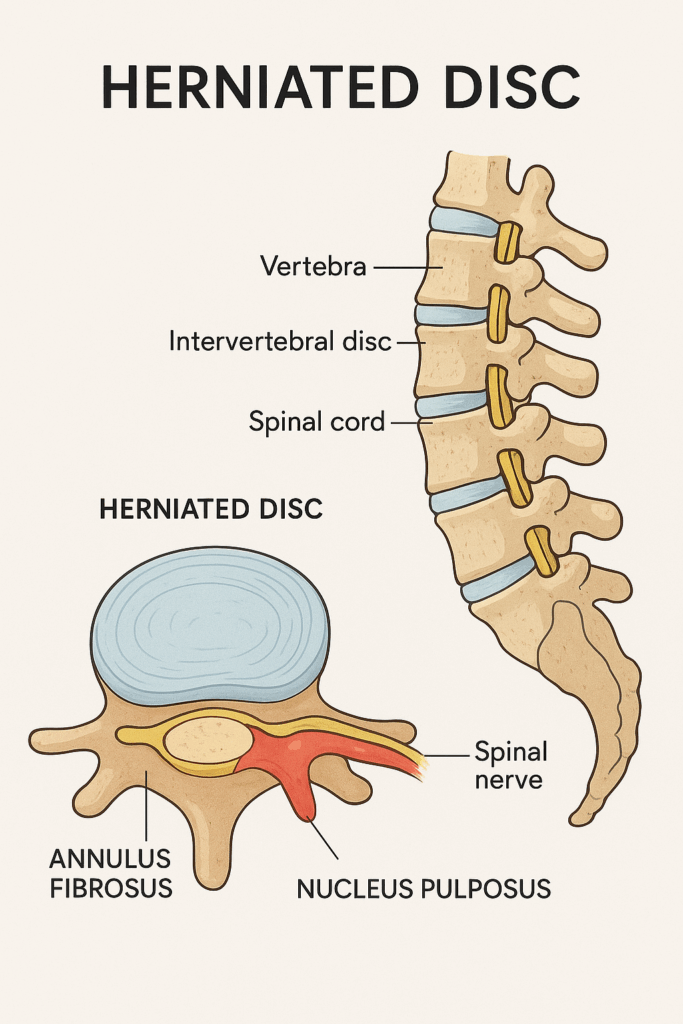
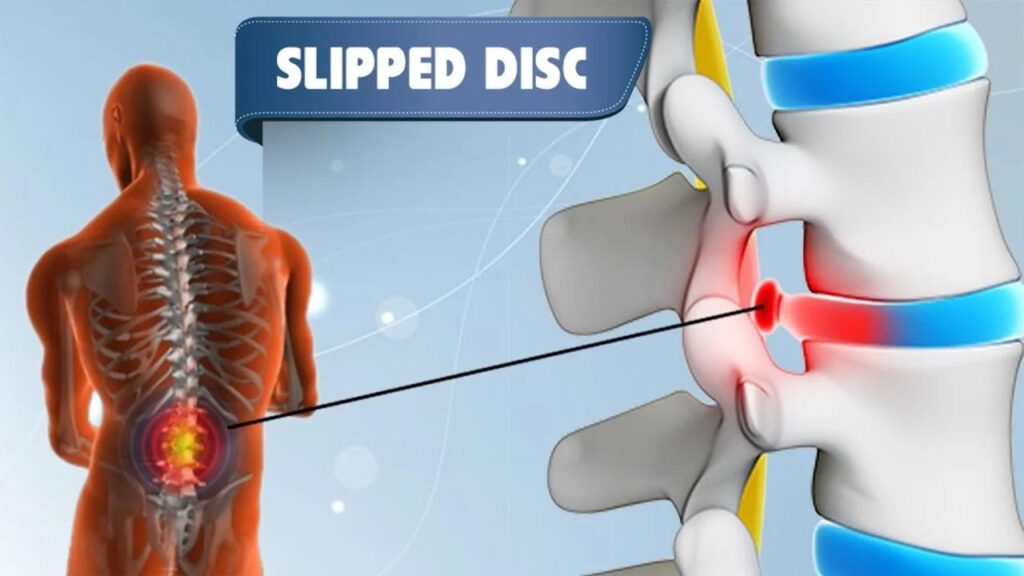
Your spine is made up of bones called vertebrae, cushioned by discs that act like shock absorbers. Each disc has a tough outer layer and a soft gel-like center. A herniated disc, also known as a slipped or ruptured disc, occurs when the inner material pushes out through a tear in the outer layer. This condition can press on nearby nerves, leading to pain, numbness, or muscle weakness.
Common Symptoms of a Herniated Disc
Recognizing the signs early can help in better treatment. Symptoms include:
- Numbness or Tingling: Reduced sensation in areas connected to compressed nerves.
- Muscle Weakness: Weakness that affects strength and motor control.
- Difficulty Walking: Pain or poor coordination while moving.
- Burning or Aching Pain: Often a sign of nerve irritation.
- Pain While Sitting or Standing: Prolonged sitting or standing may worsen discomfort.
Tip: If you experience persistent pain, consult a spine specialist immediately.
Causes: Why Do Herniated Discs Occur?
Several lifestyle and biological factors increase the risk of disc herniation:
- Poor Posture: Incorrect sitting or standing positions strain the spine.
- Prolonged Sitting: Especially with poor ergonomics.
- Heavy Lifting: Lifting incorrectly puts stress on the discs.
- Obesity: Excess weight increases pressure on the spine.
- Smoking: Reduces blood supply, weakening discs.
- Aging: Discs naturally wear down over time, losing flexibility.
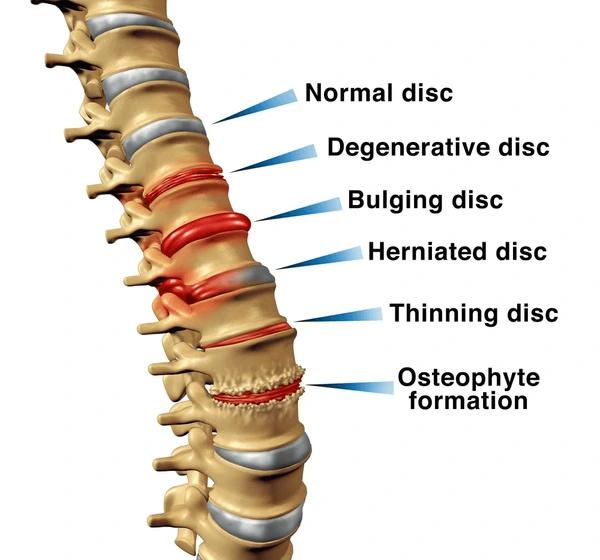
Types of Spinal Disc Conditions
Understanding the different stages of disc problems helps in diagnosis:
- Normal Disc: Healthy spine with no issues.
- Degenerative Disc: Natural wear and tear, reducing flexibility.
- Bulging Disc: Disc protrudes outward and may press on nerves.
- Herniated Disc: Outer layer ruptures and inner gel leaks out.
- Thinning Disc: Disc loses height, reducing sp1inal support.
In some cases, bone spurs (osteophytes) and endplate hardening may also develop, causing stiffness and reduced mobility.
Treatment and Prevention of Herniated Disc
- Non-Surgical Treatments: Physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, rest, hot/cold therapy, and posture correction.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Maintaining healthy weight, quitting smoking, exercising regularly, and ergonomic adjustments at work.
- Surgical Options: In severe cases, procedures like discectomy or spinal fusion may be considered.
Conclusion
A herniated disc can significantly affect your mobility and quality of life, but with early diagnosis and proper care, most patients recover without surgery. Focusing on posture, exercise, and overall spine health plays a key role in preventing disc-related issues.